Profitability analysis is a deep dive into your org’s ongoing revenue and expenses and it’s critical for SaaS businesses. The goal is to spot inefficiencies in your profit-making processes, enabling FP&A teams to boost margins by tightening earnings and eliminating unnecessary costs.
But profitability analysis is more than just looking backwards at historical data. By leveraging models that forecast future profitability, you can prioritize actions that will get your company to break-even quickest. In this way, profitability analysis acts as a guide to strategic decision-making.
Table of Contents
What is Profitability Analysis?
Profitability analysis is a detailed assessment of your business’s revenue, expenses, and the difference between them — your profit.
While it’s impossible to drive revenue without incurring expenses, your company needs to find the ideal balance between the two to ensure long-term sustainability. Profitability analysis leverages profit ratios and benchmarking to help FP&A teams do just that.
Key Components of Profitability Analysis for SaaS Businesses
The key components of profitability analysis for SaaS businesses include identifying revenue streams, assessing your costs, and then comparing the two to determine your profit and profit margins.
Profit and profit margins help you understand if you’re hitting your goals of earning more than your business is spending. They are a good indicator of when you should cut expenses or raise prices. They tell you when your product market fit is poor or when you’re ready to expand. They provide a buffer against market uncertainty and are critical for SaaS valuation.
Calculating profit margins relies on accurate data. A false profit margin based on flawed spreadsheet data can result in strategic missteps that negatively impact a company’s performance in the long term.
Automation with strategic finance tools is the first step in ensuring accurate data for profit margin calculations. It’s also critical for your financial models to adopt a real-time view, one you can constantly monitor based on your company’s actions.
Why Profitability Analysis Is Crucial for Your SaaS Business
Profitability analysis shows if your SaaS company is headed in the right direction. It helps you make the best use of limited resources, build a sustainable financial plan, and boost investor confidence. Since your primary goal is to achieve profitability, it’s crucial not to overlook this process.
Informs Strategic Decisions With Data-Driven Assets
Strategic decisions need to be backed by data. Profitability analysis must be used as an indicator of current financial health and as a running picture of the future.
A clear view of revenue and profitability is vital for sustainable growth. The SaaS rule of 40, which states your combined growth rate and profit margin should never be lower than 40%, acts as a guide to that balance for mature business models.
Understanding how costs might change as you grow is also crucial to your financial analysis. Say your company leverages a usage-based cloud model. That can cause significant fluctuations in gross profit margins. At some point, it may make sense to switch to a different hosting model or cost structure, and forecasting those situations helps you decide the best path forward.
Scenario analysis allows you to plug in different assumptions to see how they would affect profitability a month, six months, or even a year down the line.
These are just a few strategic applications that depend on a deep understanding of your profit drivers.
Identifies Areas for Growth and Improvement
Profitability analysis helps you identify areas to boost revenue and cut costs. One of the best ways to alert yourself to inefficiencies is to benchmark against past performance along with similar companies.
Your gross profit margin, for example, may be decreasing over time. If you notice a business in the same industry has a much higher gross profit margin, you need to find out why. Is there some major way of reducing costs you’re overlooking? Are they driving more revenue from a specific audience (better product-market fit?)
Another key component in understanding your profitability is understanding your expenses. Mosaic provides a view of all vendor spend, allowing you to view it down to the department level. By forecasting, you can see if you’re going over the budget you’ve allocated and which vendors are driving the variance.
How To Conduct a Comprehensive Profitability Analysis Step-By-Step
To begin your profitability analysis, you’ll need your income statement and your balance sheet. Here’s a step-by-step guide to what to do next.
Identify and Categorize Different Revenue Streams
The first step is to identify individual revenue streams. As a SaaS company, your most obvious — and most reliable — are recurring subscriptions. Once your revenue streams are identified, it’s important to forecast the expected growth around each line as well as the associated costs to support those revenue streams.
Mosaic helps you track MRR, ARR, and Revenue by connecting directly to your CRM and ERP. Mosaic gives you the ability to segment your revenue by different attributes like product lines.. This not only helps build more accurate forecasts, but also allows you to forecast the expected growth in each line of business. Each line of business may have different expense profiles required to support them, so it’s important to understand these deeply before forecasting.
Pro Tip: Remember when talking about profitability, there are different measurements of profitability. A business can be cash flow positive (profitable), or break even on a cash basis, but not profitable on a GAAP basis. This is due to the timing of revenue recognition and GAAP’s rules around recording revenue over the period of performance as it is earned, versus upfront payments spiking your cash in.
Similarly, this can work against you when paying large bills to vendors for prepayments. Large cash outflows may cause a big dip in your cash balance, but have a much softer impact on your net income due to GAAP’s treatment of expenses.
When assessing your company’s profitability, remember to consider both cash profitability and GAAP profitability.
Analyze Costs and Expenses
Break down your expenses by category: operating costs, general and administrative expenses, cost of goods sold, taxes, and so on.
For this step, it’s important to identify your cost of goods sold. Also known as cost of revenue, COGS are expenses tied directly to the production of the product. For SaaS, cost of goods sold includes factors like:
- Web hosting through AWS, Azure, or another provider
- Merchant payment processing fees
- Customer support payroll
- Cloud computing costs
Your COGS contribute to your gross profit margin, a key metric in assessing the health of software businesses. Best-in-class SaaS companies target a gross margin of 70%+.
Operating expenses will be the next biggest area of spend to explore when determining profitability. A large portion of spend will be tied directly to your people — salaries, bonuses, benefits, and taxes. It’s important to understand the intricacies related to people’s costs as these will have the biggest impact on profit or loss. A good rule of thumb is to tie per-head costs to as many line items in your P&L as possible. For instance, if you’re hiring more salespeople, make sure to include their travel and lodging costs and their applicable software licenses in your forecast.
But nailing every cost in your analysis isn’t the only thing to consider. When working through a profitability analysis, it’s important to focus on metrics that highlight ROI when analyzing costs. Let’s say you have a group of customers who are bringing in a lot of revenue, understanding how much are you spending to acquire those customers is vital to determining profitability. CAC is the perfect measurement to start with.
Once you’ve determined your CAC, you need to look at your CAC payback period. Mosaic makes this complex calculation simple, helping you track CAC payback period with pre-loaded go-to-market SaaS metrics. Your CAC payback period can help you understand how long it takes for your customers to start contributing profit to your business. Best-in-class SaaS companies target a CAC payback in 12-15 months (or less). If your CAC is outside the norm for the payback period benchmarks, these customers may not be profitable at all. In this case, the best course of action would be to spend less on sales and marketing or charge your customers a higher price to hit desired profitability.
Calculate and Interpret Key Profitability Ratios
Now that you’ve listed out your revenue and expenses, we can make sense of it all with profitability ratios.
The “big two” profit margin ratios are gross profit and net profit margin. Gross profit provides a picture of your earnings after factoring in cost of goods sold — that is, it factors in the direct costs of making your product. Net profit considers every expense. Gross profit vs. net profit is equivalent to top line vs. bottom line growth.
Operating profit also helps contextualize net profit. Since net profit includes debt and operating profit doesn’t, operating profit gives you a clearer picture of the health of your business.
Gross profit margin
Gross profit margin is concerned with how efficiently you’re producing your product. Gross profit margin shows this by subtracting your cost of goods sold (or cost or revenue) from your total earnings.
For SaaS, cost of goods sold includes things like hosting, cloud storage, and customer support headcount costs. An easy way to determine your COGS is to ask, “If we stopped producing and maintaining our product tomorrow, would this still be a cost?”
The gross profit margin formula is:
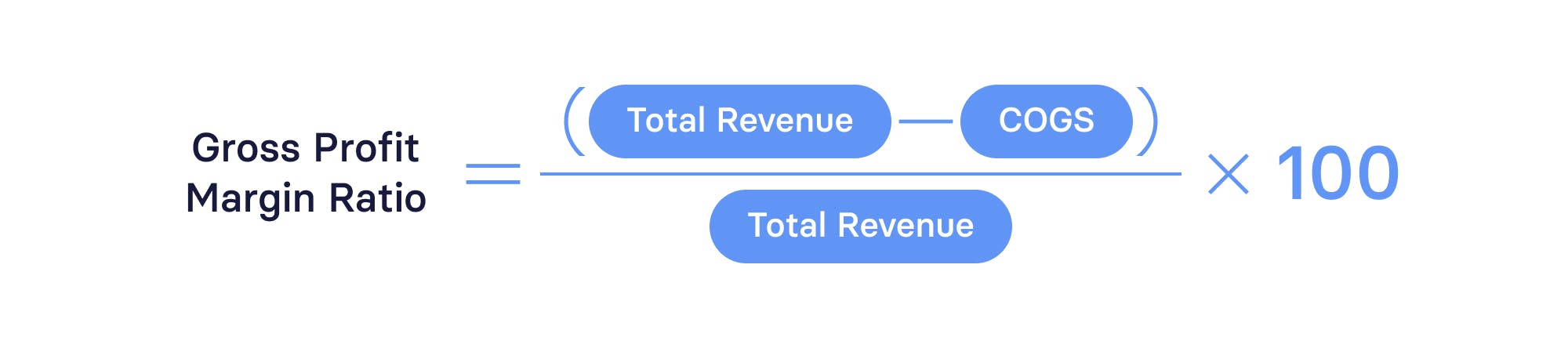
Gross profit is one of the most important financial ratios to analyze a SaaS company — it’s a snapshot of how well you’ve connected with your target audience and whether production costs are sustainable. However, since SaaS companies don’t have many direct costs compared to companies that make physical products, your gross profit margin should be considerable.
A good benchmark is 75%. Anything below 70% tends to raise concerns for investors.
Net profit margin
Net profit, also known as net income, evaluates all revenue and expenses, including taxes. It’s the bottom line on your income statement.
The formula for net profit margin is:
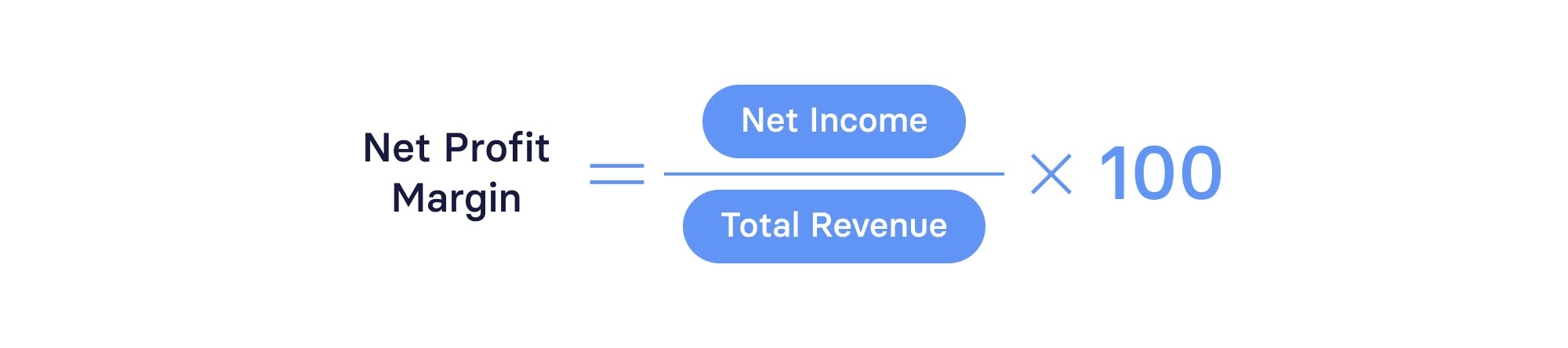
For early-stage SaaS startups, it’s common for net profit to be negative. This can be acceptable in the short term, but you’ll still want to chart a clear path toward profitability — something Mosaic’s forecasts and financial models can help with.
Operating profit margin
Operating profit margin shows you the effectiveness of your core operations in driving revenue. Operating profit margin takes into account all operating expenses, and it is also known as earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT).
The operating profit margin formula is:
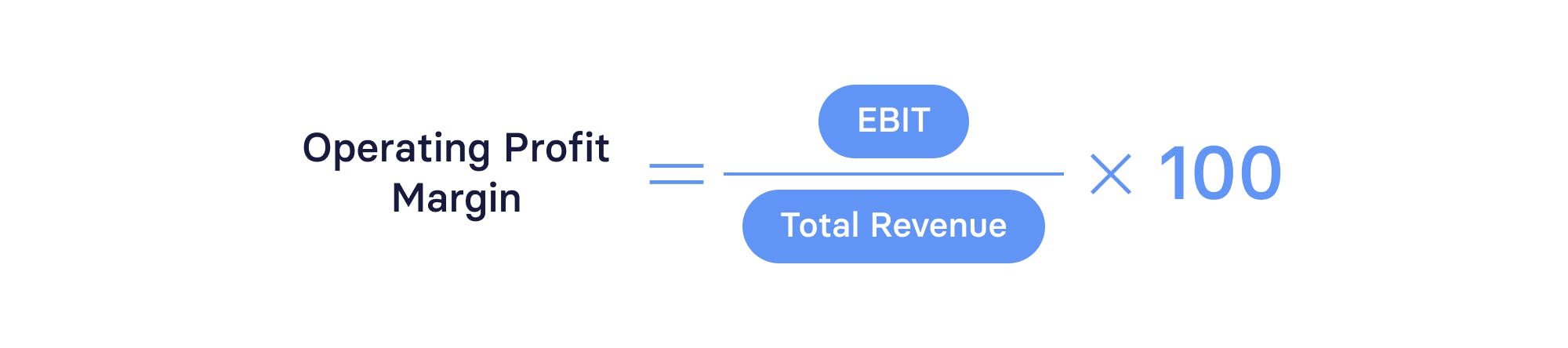
Operating profit margin is useful for determining if your business can reliably service its debt. For instance, you may have a negative net profit because of debt. But operating profit margin doesn’t take debt into account, meaning it provides a more accurate picture of your financial situation.
Return on assets
Return on assets (ROA) shows how effectively you’re driving revenue from your assets.
The formula for ROA is:
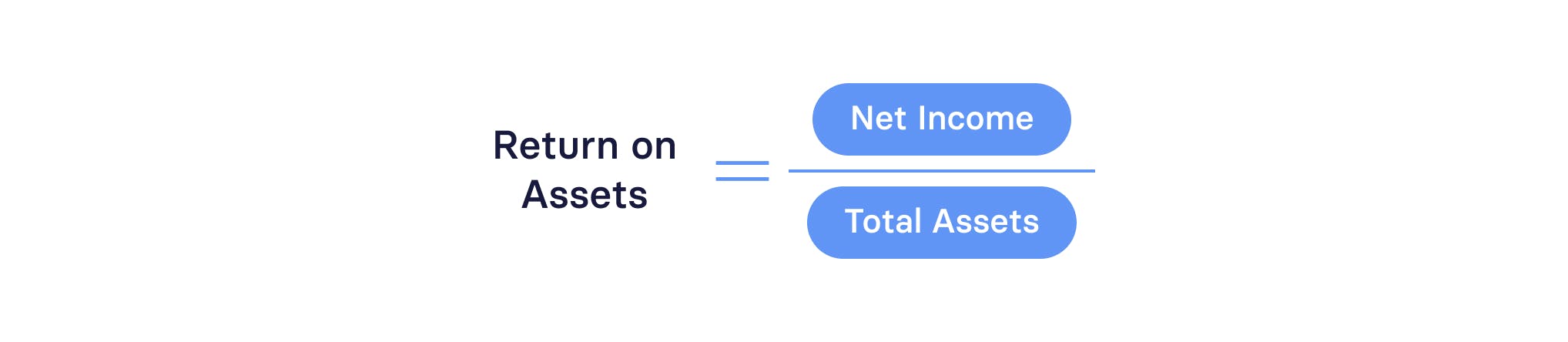
While an important profitability metric, it’s not as relevant for SaaS companies that, who don’t have many physical assets.
Return on equity
Return on equity shows how effectively your business is turning outside investment into profit.
The formula for ROE is:
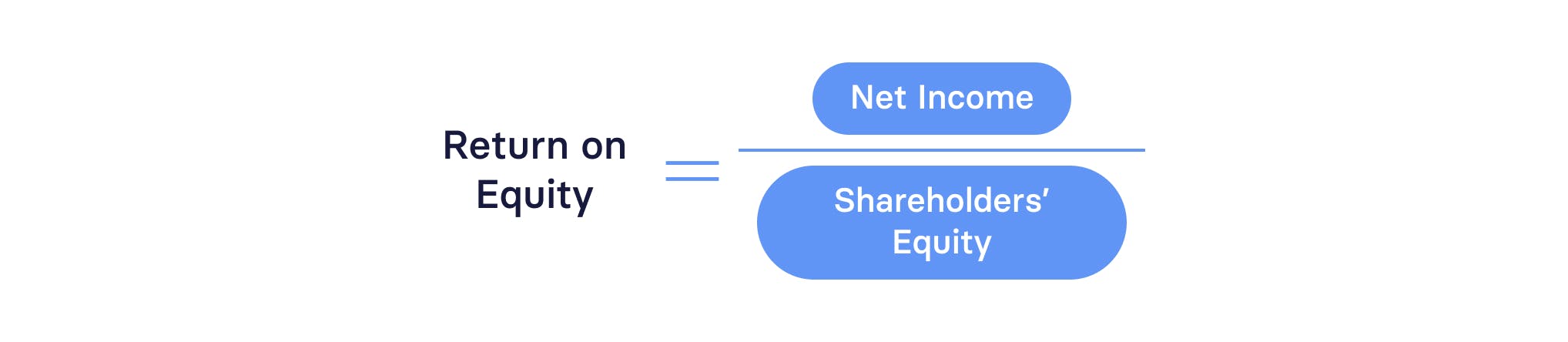
A high return on equity is excellent for attracting more funding for your company.
Interpret Your Profit Margins
The best way to interpret your profit margin results is through benchmarking against your past performance and industry averages. Are you seeing an increase in gross profit margin?
If yes, what actions have you been taking over that time period? If you’re seeing a decrease, what past actions might be responsible? Use Mosaic’s financial models to clearly visualize how your profit margins have moved over time, and cross-reference them with the specific actions taken across departments.
Perform a Break-Even Analysis
Break-even is the point at which your revenue is equal to your expenses. It’s the first step to achieving profitability. When you have a deep understanding of the pattern of your revenue and expenses, you can forecast your break-even point.
Forecasting your break-even point allows you to see how changes in different expenses move the profitability needle. A related metric is your cash flow break-even point — the point at which your cash inflows match your cash outflows.
Leverage Mosaic for Enhanced Profitability Analysis
Profitability analysis is no easy task. Still, it’s crucial for SaaS companies to do it. To get the most out of this process, leverage a strategic finance tool like Mosaic that automates tasks and displays your financial data in real time.
Integrating With Your Existing Financial Tools
To get a clear, accurate view of profitability, it doesn’t make sense to view data sets in isolation. You need to connect your CRM, ERP, billing systems, and more into one centralized platform.
As holistic FP&A software, Mosaic builds this connection. It automatically generates your gross, net, and operating profit margins based on your company’s most recent revenue and expenses. These calculations are completed using real-time data, which is gathered automatically, with no manual data entry or categorization required.
Real-Time Data for Real-Time Decisions
The real magic happens when you project those numbers into the future. Your profitability forecast acts as a lighthouse, helping FP&A teams understand the proper balance of revenue and expenses that get you to break-even, faster.
Another reason you need consolidated data? To contextualize your forecasts with scenario analysis. Scenario analysis allows you to model how changes in specific assumptions might affect your company’s profitability.
For instance, what if your pipeline predictions are 10% off? How will that affect gross and net profit? Testing the sensitivity of different levers helps you hedge your bets so that you can build a financial plan that’s solid but flexible enough to respond to changing circumstances.
At the end of the day, your business is all about earning profit. A profitability analysis helps you balance out revenue and expenses to do this as effectively as possible. A running, real-time view helps guide strategic decisions that touch on every aspect of your company.
Get started building your profitability analysis with Mosaic — Request a demo today.
Profitability Analysis FAQs
What makes profitability analysis essential for SaaS businesses?
Profitability analysis is essential for SaaS startups because they have limited resources and need to utilize those limited resources to reach profitability as quickly as possible. Profitability analysis helps you efficiently manage revenue and expenses to achieve this.
Can profitability analysis help identify new growth opportunities?
How does Mosaic simplify the profitability analysis process?
How often should a SaaS business conduct profitability analysis?
Own the of your business.